Introduction
Hello and greetings to all brothers and their sisters😜!
In this blog, I will explain the OSI Model with real-life examples and in a very simple way. I guarantee that by the end of this post, you’ll have a clear understanding of how data flows from one device to another — and how it’s all made possible because of the OSI Model.
Whether you’re a beginner or diving deep into networking, cybersecurity, or bug bounty, mastering this 7-layer model is a must for every aspiring pro.
What is the OSI Model?
Firstly, the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual communication framework ISO(International Organization for Standardization) developed the OSI Model in 1984. It was designed to standardize how different networking devices communicate with each other over a network.
The OSI model divides network communication into seven distinct layers, Each of these layers performs a specific function to ensure proper data transmission, interoperability, and troubleshooting.
This model also defines how networking devices share information with each other, enabling seamless communication between various hardware and software systems across the network.

The 7 Layers of OSI (Top to Bottom)
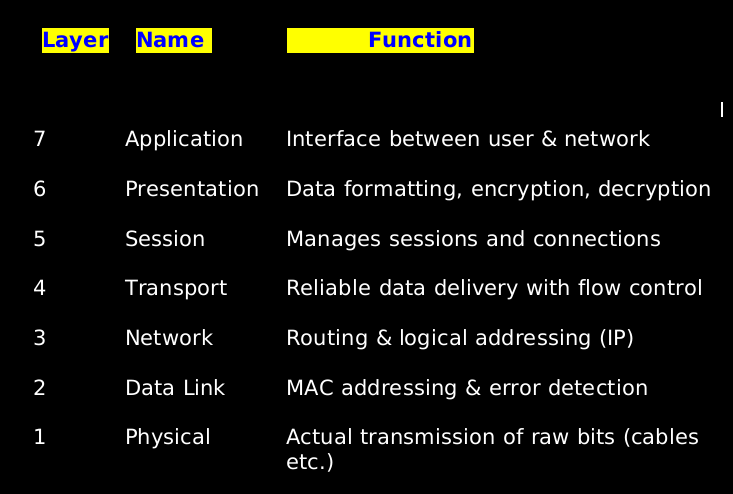
Layer-by-Layer Breakdown
1. Application Layer (Layer 7)
- Definition: This is the layer that directly interacts with the end user. It provides services for email, file transfer, and other network software services.
2. Presentation Layer (Layer 6)
- Definition: Translates data into a format the application layer understands and Handles encryption, compression, and data formatting (JSON, XML, ASCII).
- Real-life Example: Watching a video on YouTube-it’s converted into a format your system understands.
- Services: Data format conversion, encryption, compression
- Protocols: SSL/TLS, JPEG, MPEG, GIFS
3. Session Layer (Layer 5)
- Definition: Manages sessions between two devices. It establishes, maintains, and terminates connections.
- Real-life Example: When you stay logged into your bank account during a session, this layer handles the session.
- Services: Session control, dialog control
- Protocols: NetBIOS, PPTP, RPC
4. Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- Definition: Provides reliable data transfer with error correction and flow control. Ensure complete data transfer.
- Real-life Example: Like ordering food via Swiggy- the food (data) reaches you in order and complete.
- Services: Reliability, segmentation, error recovery
- Protocols: TCP,UDP,SCTP
5. Network Layer (Layer 3)
- Definition: Responsible for logical addressing and routing of data packets.
- Real-life Example: Like Google Maps showing shortest route from your home to a friend’s place.
- Services: Path determination, logical addressing
- Protocols: IP, ICMP, IGMP, IPsec, RIP, EIGRP, OSPF,
6. Data link Layer (Layer 2)
- Definition: Ensures error-free data transfer between two directly connected nodes. Converts data into frames.
- Real-life Example: Like a delivery person ensuring the right parcel is sent to the right address.
- Services: MAC addressing, error detection
- Protocols: Ethernet, PPP, ARP, VLAN
7. Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- Definition: Deals with the physical connection between devices. Transfers raw bits over the medium.
- Real-Life Example: Your Ethernet cable, WIFI signals, or fiber optics.
- Services: Bit transmission
- Protocols: Ethernet (Physical standard), USB, Bluetooth, DSL
OSI Model with Real life examples (Pizza Delivery)
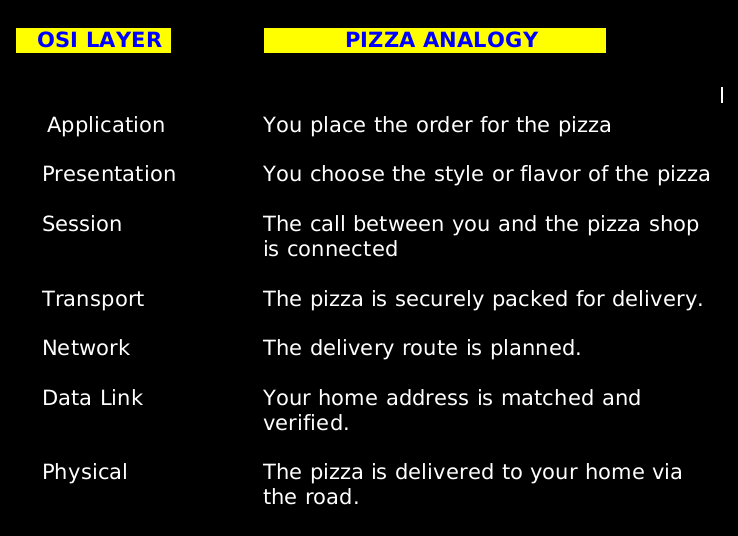
To make the OSI Model with Real Life Examples easier to digest, here’s a quick layer-by-layer summary.
Summary Table
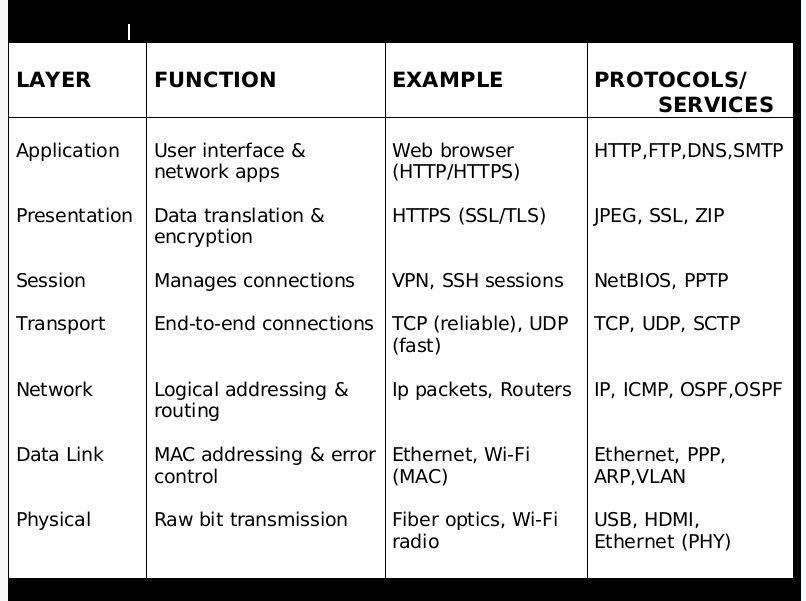
But how does this model help in real-world cybersecurity situations? Let’s find out.
OSI In Cybersecurity
- This model helps in tracing attacks. By breaking down each layer, security experts can easily identify vulnerabilities.
- Implementing security becomes easier layer-wise.
- Understanding each layer is extremely important in penetration testing.
- Every bug or vulnerability is related to some specific layer.
Advantages of OSI Model
-
Standarlized framework:
- OSI provides a universal standard for networking, making different devices and systems communicate effectively.
-
Modular Design:
- Each layer works independently, so troubleshooting and development become easier.
-
Layer-wise Troubleshooting:
- Network issues can be pinpointed to specific layers, which simplifies debugging.
-
Clear Function Distribution:
- Each layer has a defined role, reducing complexity in network design and management.
-
Promotes interoperability:
- Allow multiple vendors and systems to work together using defined protocols.
Disadvantages of OSI Model
-
Theoretical Model:
- OSI is more of a reference model; it’s not implemented exactly in real-world networks.
-
Complex implementation:
- Seven layer can sometimes be too complex and not all are needed in practice.
-
Slow Adoption:
- OSI was introduced after TCP/IP became popular, so it never fully replaced it.
-
Performance Overhead:
- Layer-by-layer processing may introduce delays and inefficiencies in some cases.
Conclusion
To sum it all up, we broke down the OSI Model with real life examples layer by layer-exactly how a hacker or cybersecurity pro should understand it. Each layer has its own unique role in how data is transmitted across networks, and with the real-life pizza delivery analogy, everything become a lot easier to grasp.
Whether you’re stepping into networking, diving into cybersecurity, or hunting bugs as a bug bounty hunter, having a strong grip on the OSI model with real life examples is absolutely essential. it helps you trace attacks, implement layer-wise security, and understand where exactly a vulnerability might live.
Your next step? Explore the real-world protocols of each layer (like TCP,IP,HTTP, DNS, ARP, etc.) and analyze their packet structure using tools like Wireshark. Theory is great – but hands-on experience is what builds real skill.
Remember:
The OSI model isn’t just a concept – it’s a story hidden inside every data packet. You just need the hacker’s eyes to read it.
![]()


One Comment